Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM672AH)
| Drug Name |
Aspirin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ACETYLSALICYLIC ACID; 50-78-2; 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid; o-Acetoxybenzoic acid; O-Acetylsalicylic acid; Polopiryna; Acylpyrin; Ecotrin; Easprin; Acetylsalicylate; Acetophen; Acenterine; Acetosal; Colfarit; Salicylic acid acetate; o-Carboxyphenyl acetate; Enterosarein; Aspergum; Salcetogen; Pharmacin; Acetosalin; Premaspin; Micristin; Benaspir; Aspirdrops; Acetonyl; Aceticyl; Temperal; Acetylin; Empirin; Ecolen; Rhodine; Endydol; Saletin; Rheumintabletten; Solprin acid; Acidum acetylsalicylicum; Globentyl; Pravigard
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Analgesics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
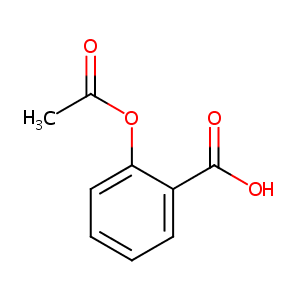 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 180.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Acute coronary syndrome | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | BA41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Aspirin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Aspirin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | Aspirin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Emerging drugs in peripheral arterial disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 Mar;11(1):75-90. | ||||
| 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4139). | ||||
| 4 | Protective Effect of Aspirin on COVID-19 Patients (PEAC) | ||||
| 5 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | Germline genetic variation in an organic anion transporter polypeptide associated with methotrexate pharmacokinetics and clinical effects. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Dec 10;27(35):5972-8. | ||||
| 9 | CYP2D6 phenotype-genotype relationships in African-Americans and Caucasians in Los Angeles. Pharmacogenetics. 1998 Dec;8(6):529-41. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199812000-00010. | ||||
| 10 | Genome-wide pharmacogenomic study of citalopram-induced side effects in STAR*D. Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Jul 3;2(7):e129. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.57. | ||||
| 11 | ITPA polymorphism affects ribavirin-induced anemia and outcomes of therapy--a genome-wide study of Japanese HCV virus patients. Gastroenterology. 2010 Oct;139(4):1190-7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.071. Epub 2010 Jul 14. | ||||
| 12 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 13 | Association between treatment-emergent suicidal ideation with citalopram and polymorphisms near cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein in the STAR*D study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007 Jun;64(6):689-97. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.64.6.689. | ||||
| 14 | Pharmacogenetics of ABCG2 and adverse reactions to gefitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Dec 6;98(23):1739-42. | ||||
| 15 | A genome-wide study identifies HLA alleles associated with lumiracoxib-related liver injury. Nat Genet. 2010 Aug;42(8):711-4. doi: 10.1038/ng.632. Epub 2010 Jul 18. | ||||
| 16 | HLA alleles influence the clinical signature of amoxicillin-clavulanate hepatotoxicity. PLoS One. 2013 Jul 9;8(7):e68111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068111. Print 2013. | ||||
| 17 | Genetic markers of suicidal ideation emerging during citalopram treatment of major depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;164(10):1530-8. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06122018. | ||||
| 18 | The human leucocyte antigen-DRB1*1302-DQB1*0609-DPB1*0201 haplotype may be a strong genetic marker for aspirin-induced urticaria. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005 Mar;35(3):339-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.02197.x. | ||||
| 19 | Cyclooxygenase inhibitors: instrumental drugs to understand cardiovascular homeostasis and arterial thrombosis. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Dec;8(4):268-77. | ||||
| 20 | A Na+-phosphate cotransporter homologue (SLC17A4 protein) is an intestinal organic anion exporter. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):C1652-60. | ||||
| 21 | Type 1 sodium-dependent phosphate transporter (SLC17A1 Protein) is a Cl(-)-dependent urate exporter. J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 20;285(34):26107-13. | ||||
| 22 | Identification of multispecific organic anion transporter 2 expressed predominantly in the liver. FEBS Lett. 1998 Jun 12;429(2):179-82. | ||||
| 23 | Caco-2 permeability, P-glycoprotein transport ratios and brain penetration of heterocyclic drugs. Int J Pharm. 2003 Sep 16;263(1-2):113-22. | ||||
| 24 | Polymorphisms of Aspirin-Metabolizing Enzymes CYP2C9, NAT2 and UGT1A6 in Aspirin-Intolerant Urticaria. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011 Oct;3(4):273-6. | ||||
| 25 | Pharmacogenomics in aspirin intolerance. Curr Drug Metab. 2009 Nov;10(9):998-1008. | ||||
| 26 | Isozyme-specific induction of low-dose aspirin on cytochrome P450 in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Mar;73(3):264-71. | ||||
| 27 | Inhibition of human phenol and estrogen sulfotransferase by certain non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Curr Drug Metab. 2006 Oct;7(7):745-53. | ||||
| 28 | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs induced endothelial apoptosis by perturbing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta transcriptional pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Nov;74(5):1399-406. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.049569. Epub 2008 Aug 4. | ||||
| 29 | Expression profile analysis of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in response to aspirin. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2005 Mar-Apr;53(2):151-8. | ||||
| 30 | DNA array analysis of the effects of aspirin on colon cancer cells: involvement of Rac1. Carcinogenesis. 2004 Jul;25(7):1293-8. | ||||
| 31 | Expression profile analysis of colon cancer cells in response to sulindac or aspirin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Mar 29;292(2):498-512. | ||||
| 32 | Aspirin regulates hepatocellular lipid metabolism by activating AMPK signaling pathway. J Toxicol Sci. 2015 Feb;40(1):127-36. doi: 10.2131/jts.40.127. | ||||
| 33 | Aspirin inhibits MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions and activities through upregulation of PPARalpha/gamma and TIMP gene expressions in ox-LDL-stimulated macrophages derived from human monocytes. Pharmacology. 2009;83(1):18-25. doi: 10.1159/000166183. Epub 2008 Oct 30. | ||||
| 34 | Effects of aspirin on metastasis-associated gene expression detected by cDNA microarray. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004 Oct;25(10):1327-33. | ||||
| 35 | Grennan DM, Ferry DG, Ashworth ME, Kenny RE, Mackinnnon M "The aspirin-ibuprofen interaction in rheumatoid arthritis." Br J Clin Pharmacol 8 (1979): 497-503. [PMID: 389264] | ||||
| 36 | Berg KJ "Acute effects of acetylsalicylic acid in patients with chronic renal insufficiency." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 11 (1977): 111-6. [PMID: 837963] | ||||
| 37 | Christensen LK, Hansen JM, Kristensen M "Sulphaphenazole-induced hypoglycemic attacks in tolbutamide-treated diabetics." Lancet 2 (1963): 1298-301. [PMID: 14071924] | ||||
| 38 | Asplund K, Wiholm BE, Lithner F "Glibenclamide-associated hypoglycaemia: a report on 57 cases." Diabetologia 24 (1983): 412-7. [PMID: 6411511] | ||||
| 39 | Hansen RA, Tu W, Wang J, Ambuehl R, McDonald CJ, Murray MD "Risk of adverse gastrointestinal events from inhaled corticosteroids." Pharmacotherapy 28 (2008): 1325-34. [PMID: 18956992] | ||||
| 40 | Davey PG "Overview of drug interactions with the quinolones." J Antimicrob Chemother 22(suppl c) (1988): 97-107. [PMID: 3053579] | ||||
| 41 | Farag MM, Mikhail MR, Abdel-Meguid E, Abdel-Tawab S "Assessment of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats treated with low doses of ibuprofen and diclofenac sodium." Clin Sci 91 (1996): 187-91. [PMID: 8795442] | ||||
| 42 | Miner PB Jr, Fort JG, Zhang Y. Intragastric acidity and omeprazole exposure during dosing with either PA32540 (enteric-coated aspirin 325?mg + immediate-release omeprazole 40?mg) or enteric-coated aspirin 325?mg + enteric-coated omeprazole 40?mg - a randomised, phase 1, crossover study.?Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;38(1):62-71. [PMID: 23692061] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Avelox (moxifloxacin) Bayer, West Haven, CT. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Actonel (risedronate). Procter and Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Cincinnati, OH. | ||||
| 45 | Abdel-Rahman MS, Reddi AS, Curro FA, Turkall RM, Kadry AM, Hansrote JA "Bioavailability of aspirin and salicylamide following oral co-administration in human volunteers." Can J Physiol Pharmacol 69 (1991): 1436-42. [PMID: 1777842] | ||||
| 46 | Bannister SJ, Houser VP, Hulse JD, Kisicki JC, Rasmussen JG "Evaluation of the potential for interactions of paroxetine with diazepam, cimetidine, warfarin, and digoxin." Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 350 (1989): 102-6. [PMID: 2530759] | ||||
| 47 | Barrow MV, Quick DT, Cunningham RW "Salicylate hypoprothrombinemia in rheumatoid arthritis with liver disease. Report of two cases." Arch Intern Med 120 (1967): 620-4. [PMID: 6054600] | ||||
| 48 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 49 | Ponce SP, Jennings AE, Madias NE, Harrington JT "Drug-induced hyperkalemia." Medicine (Baltimore) 64 (1985): 357-70. [PMID: 2865667] | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Lovenox (enoxaparin). Rhone-Poulenc Rorer, Collegeville, PA. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Xarelto (rivaroxaban). Bayer Inc, Toronto, IA. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Panhematin (hemin). Recordati Rare Diseases Inc, Lebanon, NJ. | ||||
| 53 | Heck AM, DeWitt BA, Lukes AL "Potential interactions between alternative therapies and warfarin." Am J Health Syst Pharm 57 (2000): 1221-7 quiz 1228-30. [PMID: 10902065] | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Cerebyx (fosphenytoin). Parke-Davis, Morris Plains, NJ. | ||||
| 55 | Cowan RA, Hartnell GG, Lowdell CP, Baird IM, Leak AM "Metabolic acidosis induced by carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and salicylates in patients with normal renal function." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 289 (1984): 347-8. [PMID: 6432091] | ||||
| 56 | EMEA "EMEA public statement on leflunomide (ARAVA) - severe and serious hepatic reactions.". | ||||
| 57 | Caruso V, Iacoviello L, Di Castelnuovo A, et.al "Thrombotic complications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies comprising 1752 pediatric patients." Blood 108 (2006): 2216-22. [PMID: 16804111] | ||||
| 58 | Product Information. Brukinsa (zanubrutinib). BeiGene USA, Inc, San Mateo, CA. | ||||
| 59 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 60 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Effient (prasugrel). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 62 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Acular (ketorolac). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Flolan (epoprostenol). Glaxo Wellcome, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 65 | Abebe W "Herbal medication: potential for adverse interactions with analgesic drugs." J Clin Pharm Ther 27 (2002): 391-401. [PMID: 12472978] | ||||
| 66 | Bodiford AB, Kessler FO, Fermo JD, Ragucci KR "Elevated international normalized ratio with the consumption of grapefruit and use of warfarin." SAGE Open Med Case Rep 0 (2013): 1-3. [PMID: 27489634] | ||||
